The ABCs of B12: Understanding Vitamin B12 Benefits
Why Vitamin B12 is Your Wellness Ally

If you're wondering what is vitamin B12 good for , you've come to the right place. This powerful nutrient is an absolute must for your body's daily operations, acting as a vital spark that keeps many systems running smoothly.
Here’s a quick look at its top benefits:
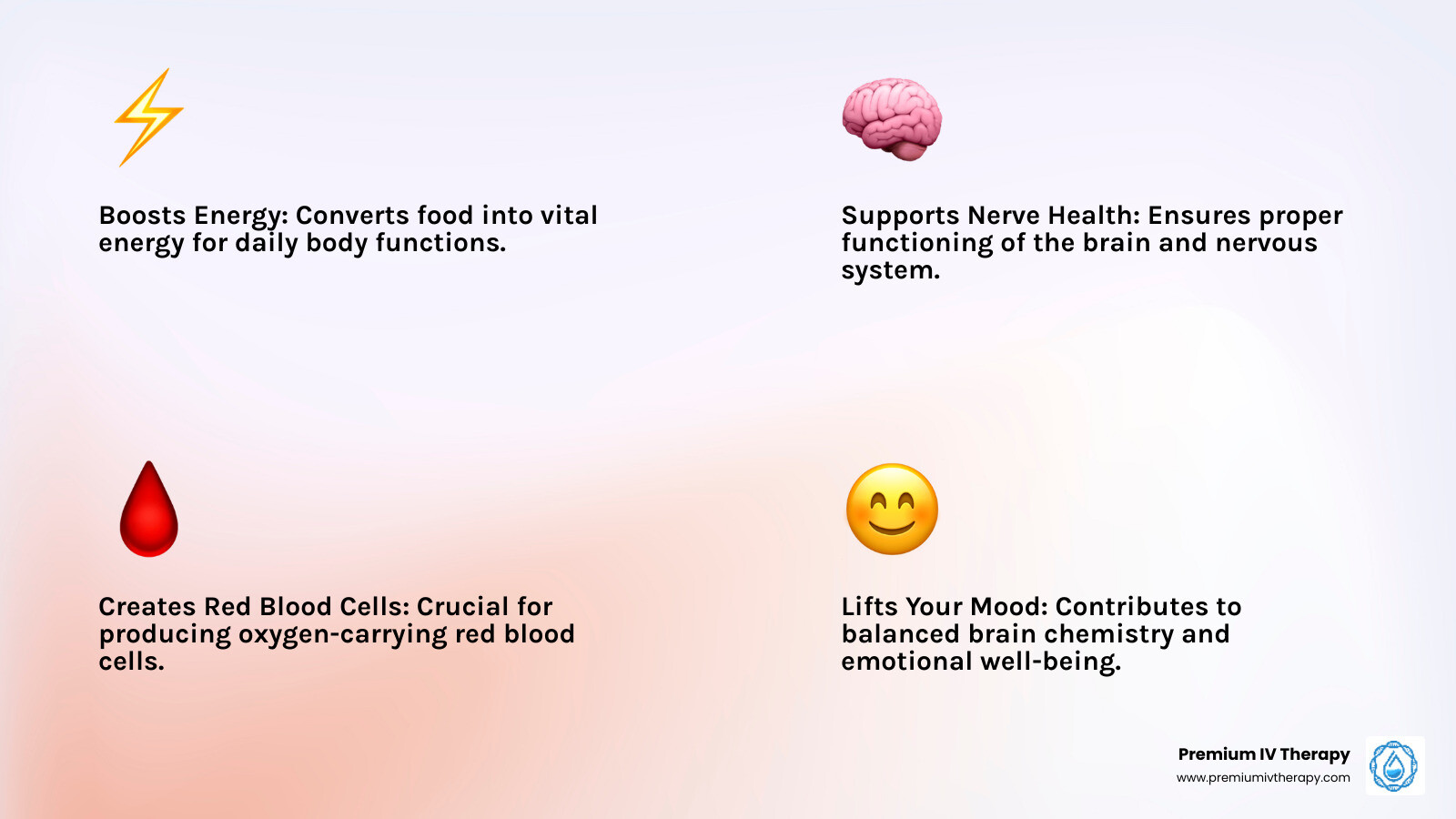
- Boosts Energy : Helps convert food into usable energy.
- Supports Nerve Health : Maintains the health of your brain and nerves.
- Creates Red Blood Cells : Essential for producing healthy red blood cells to carry oxygen.
- Aids DNA Production : Plays a key role in building your genetic material.
- Lifts Your Mood : Contributes to healthy brain chemistry and emotional balance.
Vitamin B12, or cobalamin, is a unique, water-soluble nutrient your body can't produce. You must get it from your diet or supplements. For busy professionals, understanding B12 can be a game-changer, helping you stay sharp, energetic, and ready to tackle your day.
Let's explore how this essential vitamin impacts your health.
What is Vitamin B12 and Why is it Essential?
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin , is a vital water-soluble vitamin essential for numerous bodily processes. Your body uses what it needs and excretes the rest, though it cleverly stores a reserve in the liver. This means a regular supply from diet or supplements is crucial for keeping you at your best.
So, what is vitamin B12 good for at its core? It works tirelessly behind the scenes in several key areas:
- Nerve and Brain Health: B12 is crucial for your nervous system. It helps maintain the myelin sheath , the protective coating around nerve cells that ensures messages travel quickly and efficiently throughout your brain and body. This supports everything from memory to mood.
- Energy Production: B12 is a key player in converting the food you eat—carbs, fats, and proteins—into usable energy for your cells. Without enough B12, this process can slow down, leading to fatigue.
- DNA Synthesis: Every cell in your body contains DNA, and B12 is essential for creating and repairing it. This process is vital for healthy cell growth and replenishment.
- Red Blood Cell Formation: Your body needs B12 to produce healthy red blood cells, which transport oxygen. Without enough, your body can't make these cells effectively, leading to a type of anemia that causes fatigue and weakness.
In short, Vitamin B12 is fundamental for the proper function of your brain, nerves, and blood cells. For a deeper dive, you can explore Scientific research on B12's role in the body.
The Science of Absorption: How Your Body Uses B12
Understanding how your body absorbs B12 helps explain why some people become deficient even with a good diet. It's a two-step process:
- Stomach Acid Release: When you eat B12-rich foods, the vitamin is bound to protein. Stomach acid separates the B12 from this protein.
- Intrinsic Factor Pairing: Once free, B12 binds with a protein called intrinsic factor , which is made in the stomach. This pair then travels to the small intestine , where it's absorbed into the bloodstream.
Your body stores a significant amount of B12 in the liver , enough to last for a few years. This is why a dietary deficiency can take a long time to show symptoms.
However, problems with stomach acid or intrinsic factor production can lead to food-cobalamin malabsorption , where the body can't extract B12 from food. The bioavailability of B12 also varies by food source; it's absorbed better from meat and fish than from eggs. This highlights that B12 intake isn't the only factor—proper absorption is just as important.
Recognizing and Addressing Vitamin B12 Deficiency
While severe B12 deficiency is not widespread, a larger portion of the population, particularly older adults, has insufficient levels. It's estimated that up to 15% of people may have a deficiency, with rates increasing with age. Knowing the signs and risk factors is key to maintaining your wellness.

Who is Most at Risk for Low B12 Levels?
Certain groups are more likely to develop a B12 deficiency, often due to issues with absorption rather than diet alone.
- Older Adults : Reduced stomach acid production can make it difficult to absorb B12 from food.
- Vegetarians and Vegans : B12 is found almost exclusively in animal products, increasing the risk for those on strict plant-based diets without supplementation.
- Individuals with Pernicious Anemia : This autoimmune condition prevents the body from making intrinsic factor, which is essential for B12 absorption.
- People with Gastrointestinal Conditions : Diseases like Crohn's or celiac disease can impair B12 absorption in the small intestine.
- Those Who Have Had Weight Loss Surgery : Procedures like gastric bypass alter the digestive system and can interfere with B12 absorption.
- Users of Certain Medications : Long-term use of Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) , H2 Receptor Antagonists , and the diabetes drug Metformin can reduce B12 absorption.
- Individuals with Alcohol Use Disorder : Chronic alcohol use can damage the digestive system and impair nutrient absorption.
- Pregnant Women : The need for B12 increases during pregnancy, especially for those on plant-based diets.
Common Symptoms of a Deficiency
B12 deficiency symptoms can develop slowly over years and are often subtle at first. Common signs include:
- Fatigue and Weakness : Caused by a lack of healthy red blood cells ( megaloblastic anemia ).
- Pale or Jaundiced Skin : Due to issues with red blood cell production.
- Shortness of Breath and Dizziness : A result of the body not getting enough oxygen.
- Nerve Problems : Sensations like numbness or tingling ("pins and needles") in the hands and feet, muscle weakness, or difficulty with balance.
- Mouth Issues : A sore, red tongue ( glossitis ) or mouth ulcers.
- Psychological Changes : Depression, irritability, memory loss, or "brain fog."
- Other Signs : Heart palpitations, loss of appetite, and weight loss.
If you experience these symptoms, it's important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis.
How is Deficiency Diagnosed and Treated?
Diagnosing a B12 deficiency typically involves a review of your symptoms and medical history, along with blood tests :
- Serum B12 Levels : Measures the amount of B12 in your blood.
- Methylmalonic Acid (MMA) and Homocysteine : More sensitive tests where high levels can indicate a B12 deficiency.
- Complete Blood Count (CBC) : Can reveal megaloblastic anemia.
Treatment aims to restore normal B12 levels and depends on the cause and severity of the deficiency:
- Dietary Changes : For mild, diet-related deficiencies, increasing intake of B12-rich or fortified foods can help.
- Oral Supplements : High-dose oral B12 (pills or sublingual tablets) is effective for many, even some with absorption issues.
- Nasal Sprays : A prescription option for those who prefer not to take pills.
- Vitamin B12 Injections : The most direct method, bypassing the digestive system entirely. Injections are essential for severe deficiencies or malabsorption conditions like pernicious anemia.
Your healthcare provider can determine the best treatment plan for you. For those with absorption issues or seeking a fast and efficient boost, Premium IV Therapy offers micronutrient testing and clinician-crafted B12 injections to help you achieve optimal wellness.
What is Vitamin B12 Good For? A Look at the Evidence
Now that we know the basics, let's explore the proven benefits of maintaining optimal vitamin B12 levels. What is vitamin B12 good for when it comes to your daily health and mental clarity?

Proven Benefits: What is vitamin B12 good for in your daily health?
Scientific evidence supports several key benefits of vitamin B12:
- Prevents Anemia and Boosts Energy : B12 is essential for red blood cell formation . Without it, the body produces large, ineffective cells, leading to megaloblastic anemia, fatigue, and weakness. Adequate B12 ensures your body has plenty of oxygen-carrying red blood cells, which is why many people associate it with an energy boost . Correcting a deficiency can significantly improve energy levels, but extra B12 is unlikely to provide more energy if your levels are already normal.
- Supports Bone Health : Low B12 levels have been linked to reduced bone density and a higher risk of osteoporosis. Maintaining healthy levels may help support your skeletal system, especially as you age.
- Improves Mood : B12 plays a role in synthesizing brain chemicals that regulate mood. Some studies suggest that B12 supplements, taken with antidepressants, may help improve symptoms of depression.
The Brain Connection: What is vitamin B12 good for regarding cognitive function?
Vitamin B12 is a crucial nutrient for brain health.
It is essential for nerve cell health and helps maintain the myelin sheath that allows for rapid nerve signaling. B12 also helps break down homocysteine , an amino acid that, at high levels, is linked to an increased risk of cognitive decline and dementia.
Correcting a B12 deficiency can often reverse associated memory loss . While low B12 is linked to a higher risk of dementia, there is not yet conclusive evidence that B12 supplements can prevent or treat dementia in people who are not deficient. For more information, you can review Research on B-vitamins and cognitive impairment.
Separating Fact from Fiction: Unproven Claims
It's important to distinguish proven benefits from popular myths. For people who are not deficient, there is no strong evidence that vitamin B12 supplementation will:
- Promote Weight Loss : B12 does not directly cause weight loss, though correcting a deficiency may boost energy for exercise.
- Improve Athletic Performance : Extra B12 does not provide an energy surge or improve performance in athletes with normal levels.
- Prevent Heart Disease : While B12 helps lower homocysteine, studies show B12 supplements do not reduce the overall risk of heart disease or stroke.
- Prevent Cancer : Research on B12 and cancer is mixed and inconclusive. It is not a proven method for cancer prevention.
How to Get Enough Vitamin B12
Ensuring you get enough vitamin B12 is a cornerstone of good health, and it can be achieved through diet or supplements.
Recommended Daily Intake and Food Sources
The amount of vitamin B12 you need, measured in micrograms (mcg), varies by age. Here are the Recommended Dietary Allowances (RDAs):
| Age Group | Recommended Daily Amount (mcg) |
|---|---|
| Infants (0-6 months) | 0.4 (AI) |
| Infants (7-12 months) | 0.5 (AI) |
| Children (1-3 years) | 0.9 |
| Children (4-8 years) | 1.2 |
| Children (9-13 years) | 1.8 |
| Teens (14-18 years) | 2.4 |
| Adults (19+ years) | 2.4 |
| Pregnant Teens and Women | 2.6 |
| Breastfeeding Teens and Women | 2.8 |
*AI = Adequate Intake
Vitamin B12 is found naturally almost exclusively in animal products . Top sources include:
- Seafood : Clams, tuna, and salmon are packed with B12.
- Organ Meats : Beef liver is one of the richest sources.
- Meat and Poultry : Beef and chicken provide good amounts.
- Eggs and Dairy : Milk, cheese, and yogurt are great options.
For those on plant-based diets, fortified foods are excellent sources. Check the labels on breakfast cereals , nutritional yeast , and plant-based milks (like soy or almond) for added B12. You can find detailed nutrient information on the USDA's FoodData Central.
A Guide to Vitamin B12 Supplements
Supplements are a helpful tool for those at risk of deficiency or with absorption issues. They come in several forms and types:
- Types : Cyanocobalamin is the most common and stable form found in supplements. Methylcobalamin is a naturally active form that some people prefer. Other forms include hydroxocobalamin (often used in injections) and adenosylcobalamin .
- Methods : Supplements are available as oral pills , sublingual tablets that dissolve under the tongue, prescription nasal sprays , and injections (shots) . Injections are highly effective as they bypass the digestive system, making them ideal for severe deficiencies or malabsorption.
When choosing a supplement, look for products with third-party verification, such as NSF certification or GMP certification , to ensure quality and purity. Always consult your healthcare provider before starting a new supplement regimen.
Safety, Side Effects, and Drug Interactions
One of the best things about vitamin B12 is that it's incredibly safe. As a water-soluble vitamin, your body takes what it needs and flushes out any excess in your urine. For this reason, there is no established Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL), meaning there's no known toxic dose for healthy individuals.
While B12 is very safe, extremely high doses might, in rare cases, cause mild side effects like headache, nausea, or diarrhea. Rare allergic reactions, particularly to B12 injections, can also occur. Overall, the risk of side effects from B12 supplementation is very low.
Drug Interactions
Some common medications can interfere with your body's ability to absorb vitamin B12 from food. It's important to be aware of these interactions if you are taking any of the following long-term:
- Acid-Reducing Drugs : Medications like Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) (e.g., omeprazole) and H2 Receptor Antagonists (e.g., cimetidine) reduce the stomach acid needed to release B12 from food.
- Metformin : This common diabetes medication can decrease B12 absorption over time.
- Other Medications : The antibiotic chloramphenicol , gout medication colchicine , and aminosalicylic acid can also interfere with B12.
- Vitamin C Supplements : Taking large doses of vitamin C at the same time as B12 may reduce its availability. It's best to take them a few hours apart.
Always discuss your medications and supplements with your healthcare provider to ensure they are working together safely and effectively for your health.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vitamin B12
Let's answer some of the most common questions about vitamin B12 to help you better understand this essential nutrient.
Can you take too much Vitamin B12?
It is very difficult to take too much vitamin B12. Because it is water-soluble , your body absorbs what it needs and excretes any excess through urine. This is why no Tolerable Upper Intake Level (UL) has been set for B12. While it's considered safe even at high doses, it's always wise to consult with a doctor before starting any high-dose therapy to determine the right amount for your specific health needs.
How long does it take to feel the effects of B12 supplements?
The time it takes to feel the benefits of B12 varies. It depends on the severity of your deficiency , the method of administration , and the type of symptoms you have.
If you are very deficient, you might feel an increase in energy within a few days to a week, especially with B12 injections. However, neurological symptoms like numbness or tingling can take weeks or even months to improve as nerves slowly heal. Be patient and consistent with your treatment plan, and consult your provider to monitor your progress.
Is a B12 injection better than an oral pill?
This is an excellent question, and the answer depends on the cause of your B12 deficiency. Neither method is universally "better," but one may be right for you.
-
B12 injections are essential for individuals with malabsorption issues . This includes those with pernicious anemia, Crohn's disease, or who have had weight loss surgery. Because injections bypass the digestive system, they are the most effective way to deliver B12 directly into the bloodstream. They also work faster to correct severe deficiencies. Many clinicians prefer using methylcobalamin , the active form of B12, in injections for optimal use by the body.
-
Oral pills are highly effective for correcting deficiencies caused by inadequate dietary intake , which is common in some vegetarian or vegan diets. They are convenient and can be taken at home. Interestingly, very high-dose oral supplements (1,000–2,000 mcg) can also work for some people with absorption problems, as a small amount can be absorbed passively without intrinsic factor.
The best method is the one that effectively resolves your deficiency. A consultation with a healthcare professional can help determine the most suitable path for your health journey.
Conclusion
We've explored Vitamin B12, uncovering just what is vitamin B12 good for and why it's so essential for our vitality. From energy metabolism and red blood cell formation to supporting nerve function and mood , B12 is a fundamental building block for a healthy, clear-minded life.
We've also learned that certain groups—including older adults , vegans , and those with specific medical conditions —are at a higher risk of deficiency. Recognizing symptoms like persistent fatigue or cognitive fogginess is the first step toward addressing a potential shortfall.
Your body is unique. If you suspect your B12 levels are low or simply want to optimize them for peak performance, consulting a healthcare professional is the wisest move. They can use micronutrient testing to identify your specific needs and recommend the most effective treatment.
For those seeking a direct and highly efficient way to replenish B12, especially with absorption issues, Premium IV Therapy offers clinician-crafted B12 injections in Mesa, Tempe, Phoenix, and across the East Valley. Our personalized approach ensures you get exactly what your body needs, delivered effectively.
Ready to feel the difference? Learn more about how we can support your health journey.
More info about our Vitamin B12 Injection services